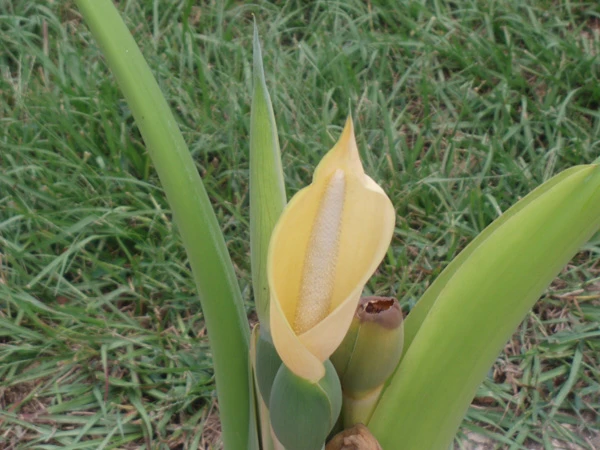
Arrowleaf Elephant’s Ear
/
(Xanthosoma sagittifolium)
Arrowleaf Elephant’s Ear (Xanthosoma sagittifolium)
/

Hedy Csakvari
CC BY 2.0




































Summary
Arrowleaf Elephant’s Ear is valued for its bold foliage and is often used in cultivation for tropical-themed gardens, as a dramatic ground cover, or as an accent plant in mixed borders. It thrives in part shade to full shade, requiring well-draining soil rich in organic matter. It is also grown for its edible corm, which is a staple in many tropical regions and can be used similarly to potatoes. However, all parts of the plant contain calcium oxalate crystals, so they must be cooked properly to avoid irritation. In some areas, it can become invasive if conditions are ideal, so gardeners should manage its spread responsibly.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Herb
- Height: 2-4 feet
- Width: 2-4 feet
- Growth Rate: Slow
- Flower Color: Green, White
- Flowering Season: Summer
- Leaf Retention: Evergreen
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Part Shade, Full Shade
- Drainage: Medium
Common Uses
Bee Garden, Edible*Disclaimer: Easyscape's listed plant edibility is for informational use. Always verify the safety and proper identification of any plant before consumption., Low Maintenance, Potted Plant
Natural Habitat
Tropical rainforests and riverbanks from Costa Rica to South Tropical America
Other Names
Common Names: Tania, Arrowleaf Elephant’s Ear, Malanga, American Taro, Blue Taro, Purple Taro, Purplestem Tannia, Purple Elephant’s Ear, New Cocoyam, Tania-Goldnarbe
Scientific Names: Xanthosoma sagittifolium, Xanthosoma atrovirens, Xanthosoma violaceum, Xanthosoma roseum, Xanthosoma mafaffa, Xanthosoma nigrum, Xanthosoma blandum, Xanthosoma xanthorrhizon, Xanthosoma atrovirens var. appendiculatum
GBIF Accepted Name: Xanthosoma sagittifolium (L.) Schott