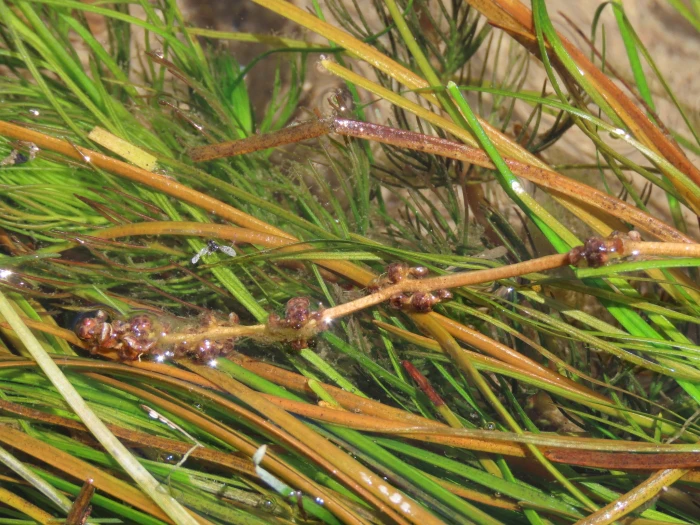
Threadleaf Pondweed
/
(Stuckenia filiformis)
Threadleaf Pondweed (Stuckenia filiformis)
/

© Nicolás Lavandero
CC BY 4.0

























Summary
Threadleaf Pondweed is valued for its ecological role in aquatic environments, providing oxygenation to the water, habitat for aquatic wildlife, and serving as a food source for waterfowl and fish. It is also used in aquariums and water gardens for its aesthetic appeal and to maintain water quality. In cultivation, it requires an aquatic setting, with full sun to part shade conditions. It can be propagated by seed or by division of rhizomes or tubers. While generally not problematic, it can become overly abundant in some conditions, potentially interfering with boating and fishing activities.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Herb
- Height: 0.3-3.3 feet
- Width: 1-3 feet
- Growth Rate: Rapid
- Flower Color: Green
- Flowering Season: Spring, Summer, Fall
- Leaf Retention: Semi-deciduous
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Full Sun, Part Shade
- Drainage: Standing
Common Uses
Low Maintenance, Water Garden
Natural Habitat
Freshwater habitats including ponds, lakes, and slowly-moving streams across the Northern Hemisphere, as well as in Hispaniola and parts of South America
Other Names
Common Names: Threadleaf Pondweed, Northern Pondweed, Slender-Leaf Pondweed, Thread-Leaved Pondweed, Alpine Thread-Leaved Pondweed, Slender-Leaved Pondweed, Fine-Leaved Pondweed, Northern Slender Pondweed
Scientific Names: Stuckenia filiformis, Coleogeton filiformis, Coleogeton filiformis subsp. alpinus, Coleogeton filiformis subsp. occidentalis, Potamogeton applanatus, Potamogeton aulacophyllus, Potamogeton austrosibiricus, Potamogeton austrosibiricus, Potamogeton fasciculatus
GBIF Accepted Name: Stuckenia filiformis