American Sycamore
/
(Platanus occidentalis)
American Sycamore (Platanus occidentalis)
/
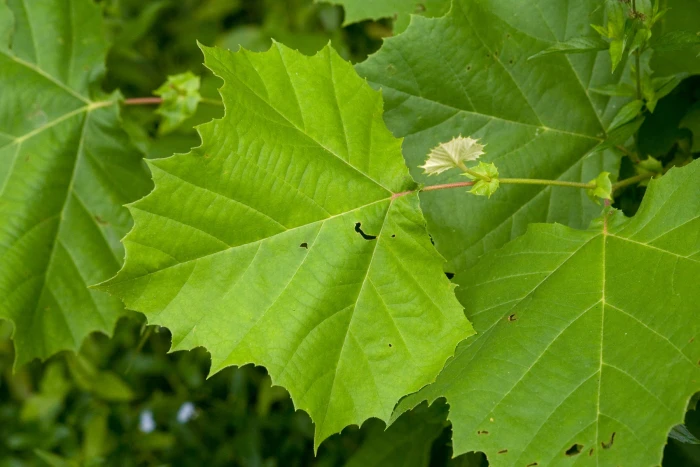

Patrick Alexander from Las Cruces, NM
CC0
Image By:
Patrick Alexander from Las Cruces, NM
Recorded By:
Copyright:
CC0
Copyright Notice:
Photo by: Patrick Alexander from Las Cruces, NM | License Type: CC0 | License URL: http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/deed.en | Uploader: Josve05a | Publisher: Wikimedia Commons | Title: Platanus_occidentalis_-_Flickr_-_aspidoscelis_(1).jpg | Notes: {{Information |Description=Findlingspark Nochten: Nymphenbaum |Source={{own}} |Date=2013-09-14 |Author= [[User:Hedwig Storch|Hedwig Storch]] |Permission= |other_versions= }} [[Category:Findlingspark Nochten]] [[C















































































Summary
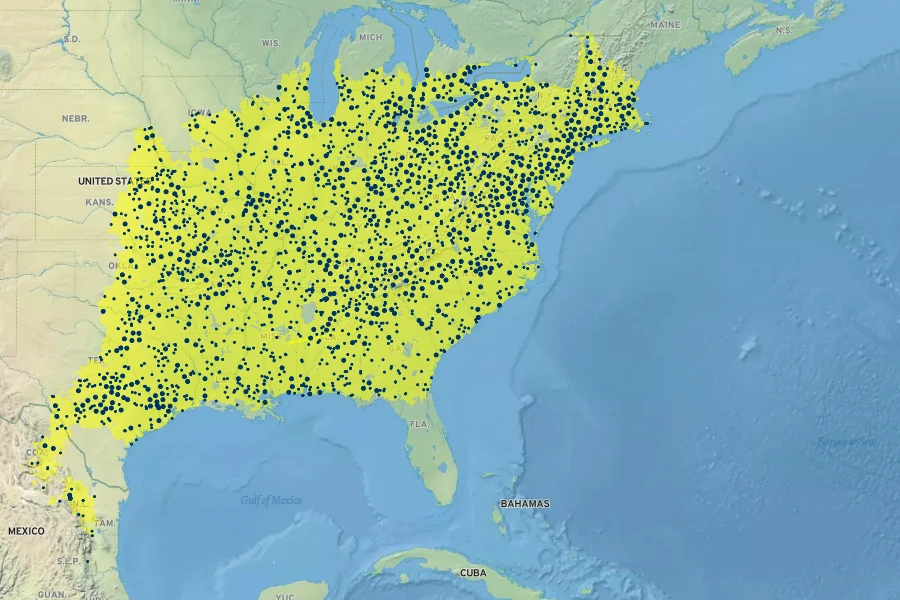
Platanus occidentalis, commonly known as American Sycamore, is a deciduous tree native to floodplain forests, riparian zones, and wetlands of the eastern and central United States, as well as the mountains of northeastern Mexico, extreme southern Ontario, and possibly extreme southern Quebec. It is often incorrectly referred to as water beech, which is a different species. The American Sycamore typically reaches heights of 75-120 feet (23-37 meters) with a broad, spreading canopy of 75-100 feet (23-30 meters). Its distinctive bark, which flakes off in large pieces to reveal a creamy white inner bark, and its large, maple-like leaves are notable features. The tree produces small, inconspicuous flowers followed by characteristic spiky seed balls.
The American Sycamore is valued for its rapid growth and tolerance of air pollution and wet soils, making it suitable for urban environments and restoration projects. It is often used as a shade tree in parks and large landscapes. This species requires full sun and can tolerate a range of soil conditions, from medium to wet, with good drainage. While it is generally easy to maintain, it can be susceptible to sycamore anthracnose and other fungal diseases, and its large size and aggressive root system can pose challenges in smaller spaces.CC BY-SA 4.0
The American Sycamore is valued for its rapid growth and tolerance of air pollution and wet soils, making it suitable for urban environments and restoration projects. It is often used as a shade tree in parks and large landscapes. This species requires full sun and can tolerate a range of soil conditions, from medium to wet, with good drainage. While it is generally easy to maintain, it can be susceptible to sycamore anthracnose and other fungal diseases, and its large size and aggressive root system can pose challenges in smaller spaces.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Tree
- Height: 75-120 feet
- Width: 40-70 feet
- Growth Rate: Moderate
- Flower Color: N/A
- Flowering Season: Spring
- Leaf Retention: Deciduous
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Full Sun
- Drainage: Fast, Medium
Common Uses
Bee Garden, Bird Garden, Butterfly Garden, Deer Resistant, Drought Tolerant, Erosion Control, Rabbit Resistant, Water Garden
Natural Habitat
Floodplain forests, riparian zones, and wetlands
Other Names
Common Names: American Planetree, Western Plane, Occidental Plane, Buttonwood, Water Beech, Nordamerikanische Platane, 양버즘나무
Scientific Names: Platanus occidentalis, Platanus palmeri, Platanus lobata, Platanus occidentalis var. occidentalis, Platanus occidentalis var. palmeri, Platanus occidentalis var. glabrata, Platanus densicoma, Platanus occidentalis f. attenuata, Platanus integrifolia, Platanus occidentalis f. occidentalis
GBIF Accepted Name: Platanus occidentalis L.