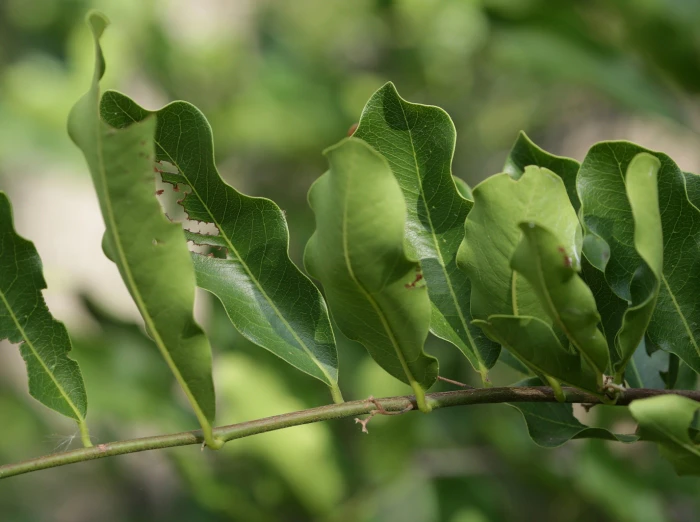
Jackalberry
/
(Diospyros mespiliformis)
Jackalberry (Diospyros mespiliformis)
/

Wynand Uys
CC BY 4.0

























Summary
Jackalberry trees are valued for their hard, termite-resistant wood, which is utilized in making durable wood floors and high-quality furniture. In cultivation, they are often used as shade trees in large landscapes or as focal points in botanical gardens. They thrive in full sun and can tolerate a range of soil types, provided they are well-drained. It can become drought-tolerant once established. Gardeners should note that due to its size and root system, it should be planted with ample space from structures.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Tree
- Height: 15-60 feet
- Width: 20-50 feet
- Growth Rate: Slow
- Flower Color: White, Yellow
- Flowering Season: Spring, Summer
- Leaf Retention: Evergreen
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Full Sun
- Drainage: Medium, Fast
Common Uses
Bird Garden, Butterfly Garden, Edible*Disclaimer: Easyscape's listed plant edibility is for informational use. Always verify the safety and proper identification of any plant before consumption., Low Maintenance
Natural Habitat
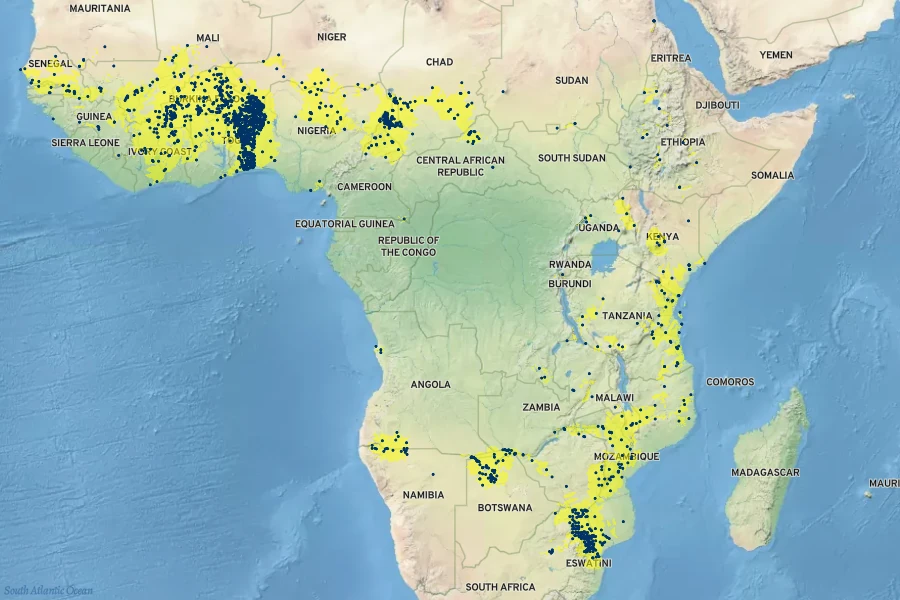
Predominantly found in the savannas and occasionally in riverine forests across Africa
Other Names
Common Names: Jackalberry, Rhodesian Ebony, Kafifi Katembo, Mufifi, Mufituamuzi, Mutomu, Tchumu, African Ebony, Cape Ebony
Scientific Names: Diospyros mespiliformis, Diospyros bicolor, Diospyros corylicarpa, Diospyros holtzii, Diospyros kilimandscharica, Diospyros mespiliformis, Diospyros sabiensis, Diospyros senegalensis, Diospyros senegalensis
GBIF Accepted Name: Diospyros mespiliformis