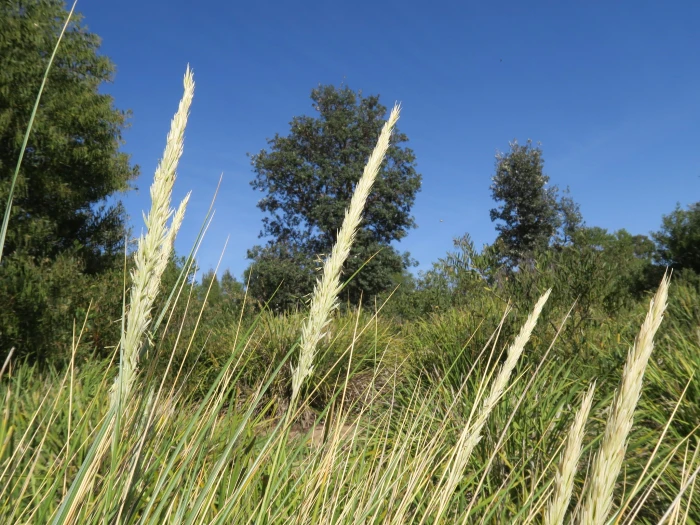
Marram Grass
/
(Ammophila arenaria)
Marram Grass (Ammophila arenaria)
/

Harry Rose
CC BY 2.0



















































Summary
Marram Grass is valued for its ability to adapt to dry sand and its role in dune formation and stabilization. Its leaves become rolled and tight when moisture levels are low, which reduces water loss and allows it to survive in arid conditions. In cultivation, it is used primarily for soil erosion control and dune stabilization. It generally does best in full sun and in soils with fast drainage. However, gardeners should be aware that Ammophila arenaria is potentially invasive in some parts of the world. It is invasive along Pacific coast dunes of North America, New Zealand, and Australia, where it alters dune ecosystems.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Grass
- Height: 2-3.5 feet
- Width: 0.8-1 feet
- Growth Rate: Moderate
- Flower Color: N/A
- Flowering Season: Summer
- Leaf Retention: Semi-deciduous
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Full Sun
- Drainage: Fast
Common Uses
Bank Stabilization, Bird Garden, Drought Tolerant, Erosion Control, Low Maintenance, Salt Tolerant
Natural Habitat
native to coastal sand dunes in Europe and North America, it thrives in open, sandy habitats where it can tolerate the harsh conditions of wind and salt spray
Other Names
Common Names: Marram, European Beach Grass, Sea Matgrass, European Beachgrass, Marramgrass, Moresg, Môr-Hesgen, Sand-Hjaelme, Gewöhnlicher Strandhafer, Helm
Scientific Names: Ammophila arenaria, Calamagrostis arenaria, Ammophila arenaria subsp. arundinacea, Psamma arenaria, Calamagrostis arenaria subsp. arundinacea, Ammophila arenaria var. arundinacea, Ammophila arundinacea, Arundo arenaria, Ammophila arundinaceae
GBIF Accepted Name: Ammophila arenaria (L.) Link