Amur Corktree
/
(Phellodendron amurense)
Amur Corktree (Phellodendron amurense)
/

Repina Tatyana
CC BY 4.0





















































Summary
Amur Corktree is valued for its ornamental bark, shade-providing canopy, and its adaptability to urban environments. It is used in traditional Chinese medicine, and the pressed oil from its fruit has applications in herbal remedies. In cultivation, it requires full sun to part shade and can tolerate a range of soil types, provided they have good drainage. It is often planted as a street tree or in parks, but care should be taken as it can become invasive outside its native range, particularly in the United States. It has been found to become invasive in many parts of North America and is listed as a noxious weed in Massachusetts.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Tree
- Height: 30-45 feet
- Width: 30-60 feet
- Growth Rate: Moderate
- Flower Color: N/A
- Flowering Season: Spring, Summer
- Leaf Retention: Deciduous
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Full Sun
- Drainage: Slow, Medium, Fast
Common Uses
Deer Resistant, Drought Tolerant, Fragrant, Low Maintenance, Rabbit Resistant, Salt Tolerant
Natural Habitat
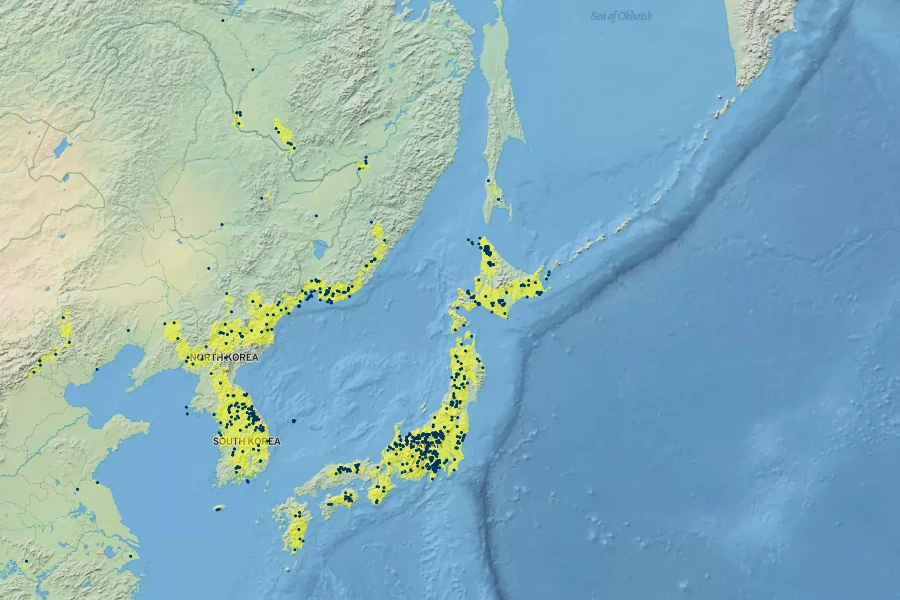
Native to mixed forests and riverbanks in East Asia
Other Names
Common Names: Chinese Corktree, Phellodendron, Arbre Liège De Chine, Arbre À Liège De L’Amour, Phellodendre De L’Amour, Phellodendron De Sibérie, Phellodendron De L’Amour, Sibiriskt Korkträd, 황벽나무, Amur Cork Tree
Scientific Names: Phellodendron amurense, Phellodendron molle, Phellodendron amurense f. molle, Phellodendron insulare, Phellodendron piriforme, Phellodendron amurense f. insulare, Phellodendron amurense var. molle, Phellodendron amurense var. suberosum, Phellodendron kodamanum
GBIF Accepted Name: Phellodendron amurense Rupr.