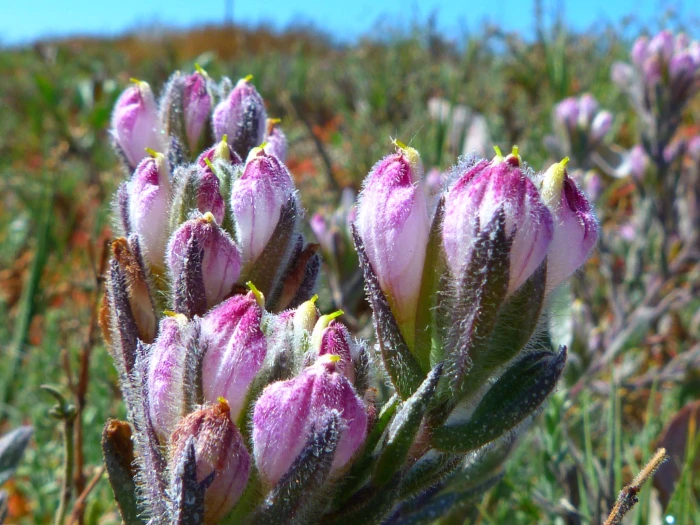
Saltmarsh Bird’s-Beak
/
(Chloropyron maritimum)
Saltmarsh Bird’s-Beak (Chloropyron maritimum)
/

Zack Abbey
CC BY 4.0
Image By:
Zack Abbey
Recorded By:
Copyright:
CC BY 4.0
Copyright Notice:
Photo by: Zack Abbey | License Type: CC BY 4.0 | License URL: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ | Rights Holder: Zack Abbey | Publisher: iNaturalist | Date Created: 2017-06-14T15:36:21-07:00 |






















Summary
Chloropyron maritimum, commonly known as Saltmarsh Bird’s-Beak, is a perennial herb that is native to the coastal salt marshes and alkaline flats of primarily in California and Baja California in Mexico. This plant is typically found in saline environments, such as coastal estuaries and salt marshes, where it plays a role in the specialized plant communities adapted to high salinity conditions. It grows at a moderate rate to a height and width of approximately 0.5-1.5 feet (0.15-0.5 meters). Saltmarsh Bird’s-Beak is characterized by its spike-like inflorescences bearing white to cream flowers, which are most prolific in the spring through fall. The flowers are adapted to attract pollinators such as bees and are considered moderately showy.
Saltmarsh Bird’s-Beak is valued for its unique appearance and its ability to thrive in saline conditions that are challenging for many other plants. It is used in restoration projects for coastal habitats and can be a distinctive addition to salt-tolerant gardens. In cultivation, it requires full sun exposure and well-draining soils, preferably clay or loam, with moderate water needs. Due to its specialized habitat requirements, it is not commonly found in general horticulture but is of interest for conservation and ecological plantings. Gardeners should be aware that this plant may require supplemental water in areas with lower salinity than its native habitat.CC BY-SA 4.0
Saltmarsh Bird’s-Beak is valued for its unique appearance and its ability to thrive in saline conditions that are challenging for many other plants. It is used in restoration projects for coastal habitats and can be a distinctive addition to salt-tolerant gardens. In cultivation, it requires full sun exposure and well-draining soils, preferably clay or loam, with moderate water needs. Due to its specialized habitat requirements, it is not commonly found in general horticulture but is of interest for conservation and ecological plantings. Gardeners should be aware that this plant may require supplemental water in areas with lower salinity than its native habitat.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Herb
- Height: 0.5-1.5 feet
- Width: 0.5-1.5 feet
- Growth Rate: Moderate
- Flower Color: Cream, White
- Flowering Season: Spring, Summer, Fall
- Leaf Retention:
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Full Sun
- Drainage: Fast
Common Uses
Low Maintenance, Salt Tolerant, Water Garden
Natural Habitat
Coastal salt marshes and alkaline flats of California and Baja California in Mexico
Other Names
Common Names: Salty bird’s-beak, Bird’s-beak
Scientific Names: Chloropyron maritimum, Chloropyron palustre
GBIF Accepted Name: Chloropyron maritimum