Bromus Tectorum
/
(Bromus tectorum)
Bromus Tectorum (Bromus tectorum)
/

© psweet
CC BY-SA 4.0
Image By:
© psweet
Recorded By:
Copyright:
CC BY-SA 4.0
Copyright Notice:
Photo by: © psweet | License Type: CC BY-SA 4.0 | License URL: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/ | Uploader: psweet | Publisher: iNaturalist |






















Summary
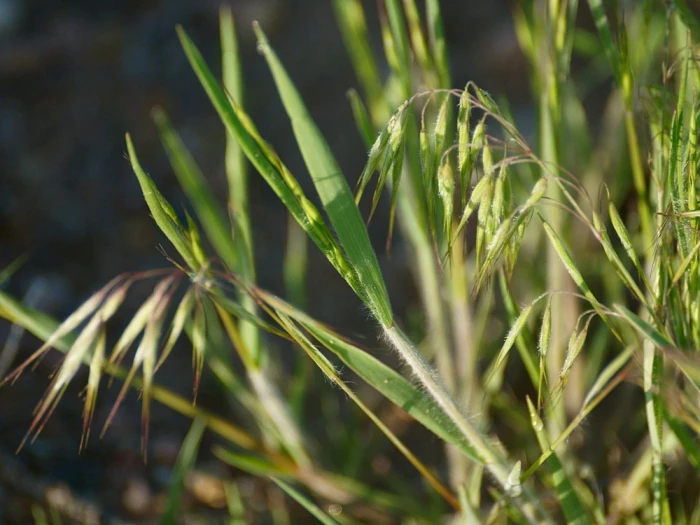
Anisantha tectorum, also known as Bromus tectorum or downy brome, is a winter annual grass native to the Mediterranean region, including Europe, southwestern Asia, and northern Africa. It typically grows to a height of 16-35 inches (40-90 cm) with smooth, slender stems and soft, hairy leaves. The inflorescence is a nodding panicle, with each spikelet containing several flowers that can vary in color from green to purplish. Downy brome is particularly noted for its ability to thrive in a variety of soil types, although it prefers sandy or loamy soils with good drainage. It is a pioneer species that quickly colonizes disturbed sites, which can lead to increased fire frequency and altered soil properties, threatening native plant communities.
Downy brome is often used for erosion control and as forage for livestock, although its nutritional value decreases rapidly after flowering. However, it is invasive and ecosystem-altering across the Intermountain West and Great Basin of North America.CC BY-SA 4.0
Downy brome is often used for erosion control and as forage for livestock, although its nutritional value decreases rapidly after flowering. However, it is invasive and ecosystem-altering across the Intermountain West and Great Basin of North America.CC BY-SA 4.0
Plant Description
- Plant Type: Grass
- Height: 0.5-2 feet
- Width: 0.5-2 feet
- Growth Rate: Rapid
- Flower Color: N/A
- Flowering Season: Spring
- Leaf Retention:
Growth Requirements
- Sun: Full Sun
- Drainage: Medium, Fast
Common Uses
Erosion Control, Low Maintenance
Natural Habitat
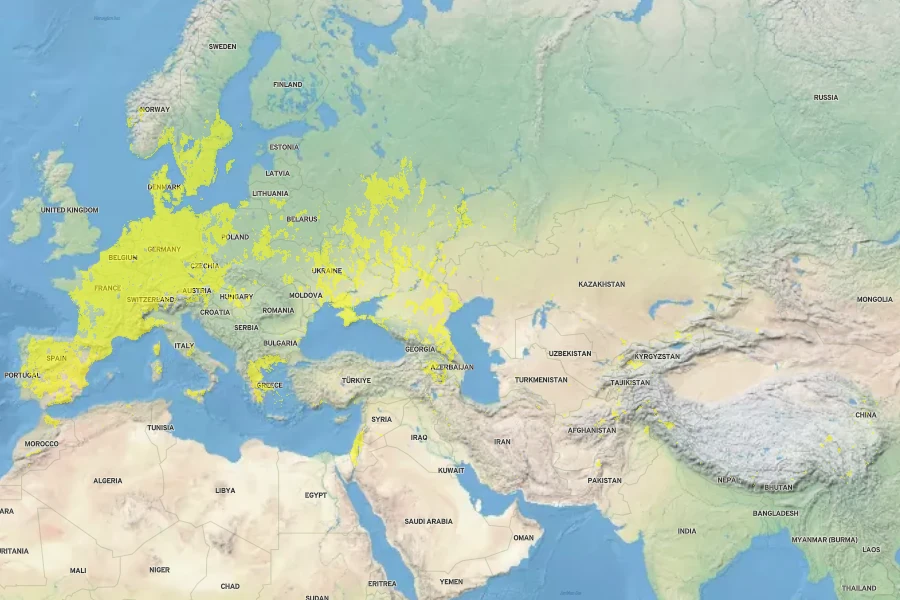
Native to the Mediterranean region, including Europe, southwestern Asia, and northern Africa
Other Names
Common Names: Cheatgrass, Drooping Brome, Dachtrespe, Downy Brome, Downy Chess
Scientific Names: Bromus tectorum, Anisantha pontica, Anisantha tectorum, Anisantha tectorum subsp. tectorum, Anisantha tectorum var. hirsuta, Anisantha ×rosettae, Bromus abortiflorus, Bromus australis, Bromus avenaceus
GBIF Accepted Name: Bromus tectorum